Solids
Explore the most stable state of matter.
Understanding Solids
Solids are characterized by their fixed shape and volume, with particles tightly packed in regular arrangements. The strong intermolecular forces hold particles in fixed positions, allowing only vibration.
Common examples include:
- Metals (Iron, Gold, Copper)
- Minerals and Crystals
- Wood and Stone
- Ice and Salt
- Glass and Ceramics
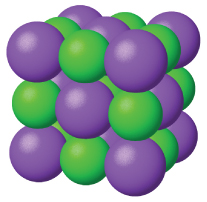
Properties of Solids
Crystal Structure
Atoms are arranged in regular, repeating patterns forming crystalline structures. This gives solids their definite shape and volume.
Molecular Motion
Particles in solids vibrate in fixed positions but don't move freely. This vibration increases with temperature.
Density
Generally have high density due to tightly packed particles with minimal space between them.
Compressibility
Very low compressibility due to strong intermolecular forces and minimal space between particles.
Visual Examples
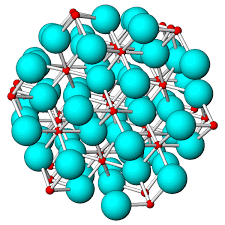
Crystal Formations
Natural crystal structures showing regular atomic arrangements.

Metallic Bonds
Microscopic view of metal atomic structure.
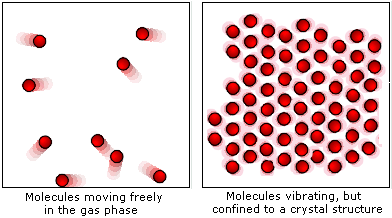
Molecular Solids
Examples of molecular solid structures.
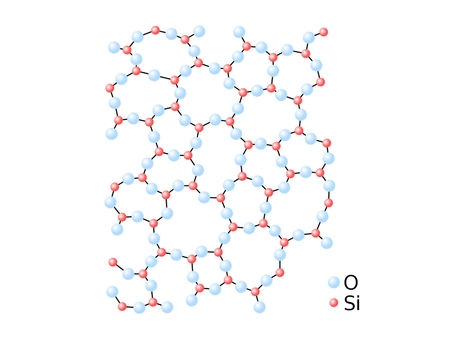
Amorphous Solids
Irregular particle arrangements in glass and plastics.
